Recently, four research advancements from the School of Cyber Science and Technology (CST) have been accepted by ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (ACM CCS 2025), a top-tier international conference in cybersecurity.
Paper 1:
Co-Prime: A Co-design Framework for Privacy Preserving Machine Learning on FPGA
The first author is Ph.D. student Xu Shuo, and the corresponding author is Associate Researcher Zhang Wei. Researcher Xu Jiming from Ant Group and Prof. Ju Lei also participated in this work. The paper proposes a Co-Prime framework for privacy-preserving machine learning based on FPGA. By jointly optimizing the protocol and hardware, it breaks through the communication bottleneck of the traditional three-party computation (3PC) secret sharing, providing a new solution for the implementation of high-performance privacy computing.
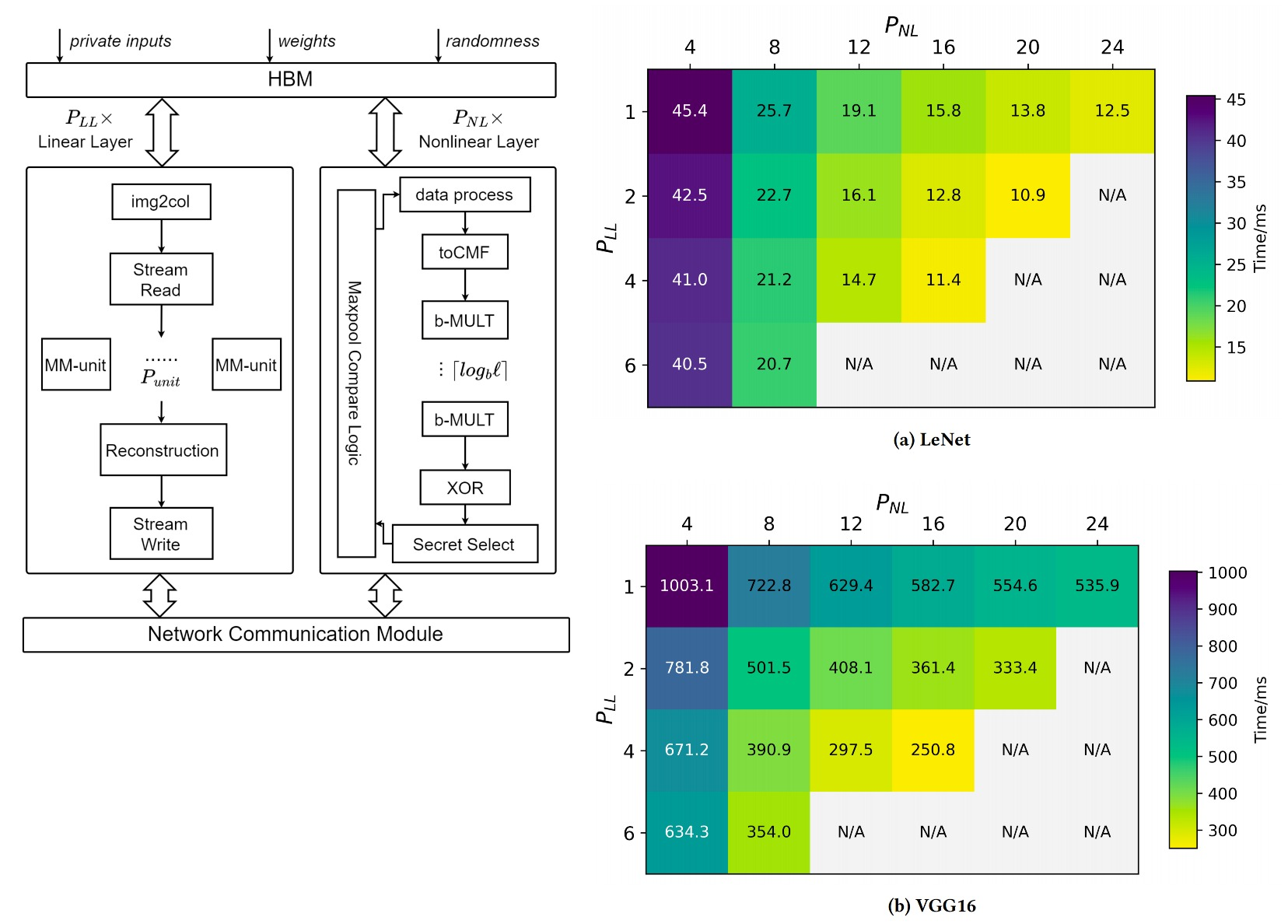
Fig 1. The Hybrid Protocol Design of Co-Prime
Paper 2:
DCMI: A Differential Calibration Membership Inference Attack Against Retrieval-Augmented Generation
The first author is master’s student Gao Xinyu, with corresponding authors Prof. Guo Shanqing and Prof. Li Zheng. Ph.D. student Meng Xiangtao also contributed significantly to this work. The paper proposes the Differential Calibration Membership Inference Attack (DCMI), which eliminates interference from non-member retrieved documents and demonstrates significant advantages over traditional approaches.
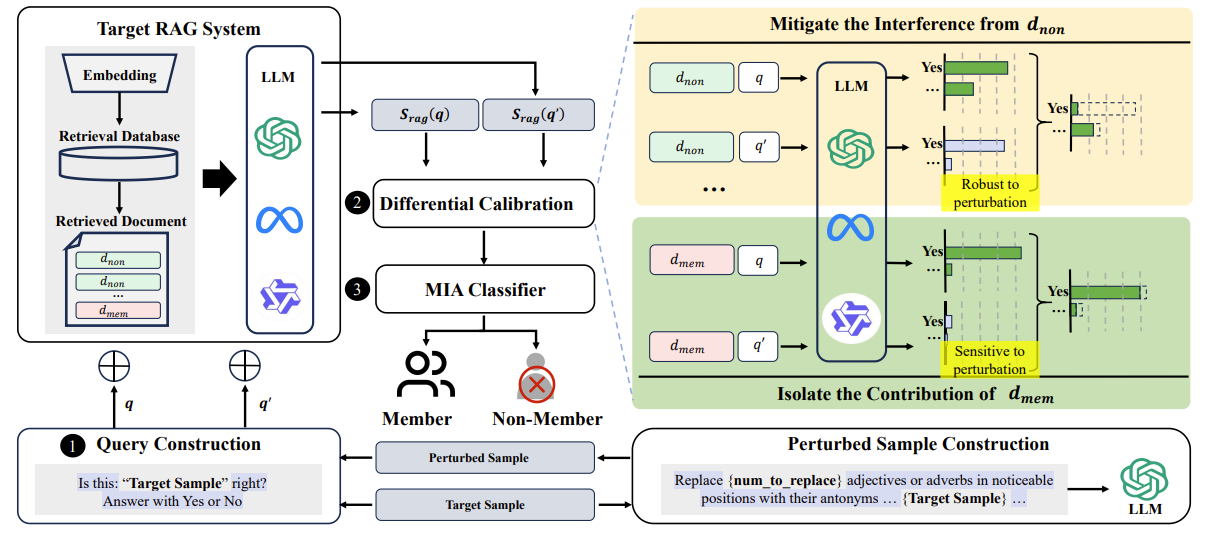
Fig 2. The Overall Architecture of the Proposed DCMI Attack
Paper 3:
Multi-Party Private Set Operations from Predicative Zero-Sharing
The first author is Ph.D. student Dong Minglang, with her supervisor Professor Chen Yu serving as the corresponding author. Zhang Cong (B.S. graduate of Shandong University), a postdoctoral researcher at Institute for Advanced Study of Tsinghua University, is the third author. Master's students Bai Yujie and Cao Yang jointly completed the experimental part of this work. This paper presents the first unified framework for Multi-Party Private Set Operations (MPSO) with strong security, generic functionality, and high performance, breaking through the limitations of existing protocols.
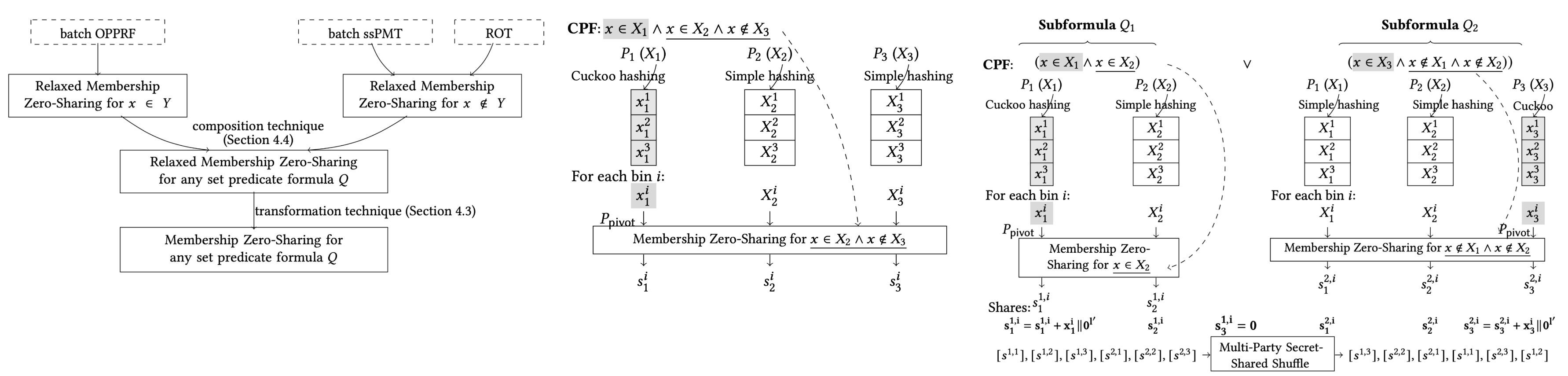
Fig 3. An MPSO Framework Supporting Arbitrary Compositions of Set Operations
Paper 4:
Threshold ECDSA in Two Rounds
The first author is master’s student Lyu Yingjie, and the corresponding author is Assoc. Prof. Li Zengpeng. Assoc. Prof. Hong-Sheng Zhou at Virginia Commonwealth University and Ph.D. student Deng Xudong also made contributions. This work presents the first threshold ECDSA signing protocol that only takes two rounds of interaction, with two technical contributions. First, a key component underlying prior schemes called “multiplication to addition” is optimized from two rounds to one. Second, using a mechanism of “presignature rerandomization”, which is more round-efficient, the protocol achieves immunity to a known degradation of security.
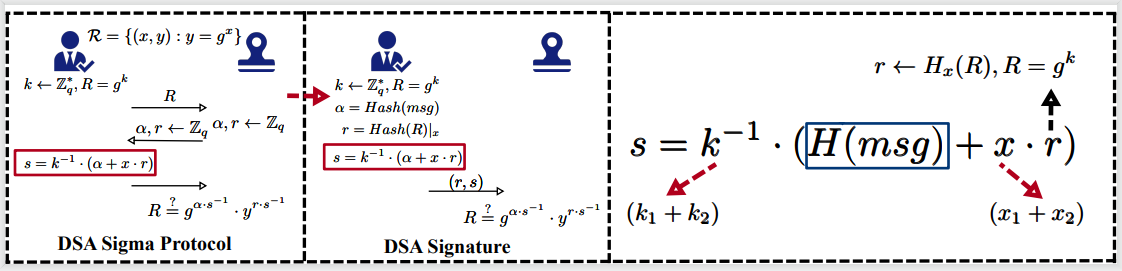
Fig 4. Structure of ECDSA Visualized
About ACM CCS
Alongside IEEE S&P, USENIX Security, and NDSS, ACM CCS is recognized as one of the four top-tier conferences in cybersecurity. It is classified as a Category A conference by the China Computer Federation (CCF) and holds significant influence in both academia and industry. Over the past decade, ACM CCS has maintained an average acceptance rate of approximately 18%, with accepted papers representing cutting-edge advancements and technological breakthroughs in cybersecurity. So far this year, five papers from CST have been accepted by ACM CCS 2025.